Running head: COPING,
PERSONALITIES, AND STRESS LEVEL
Coping Styles Used by Introverts and Extroverts in
Varying Stress Situations.
Daniella Posella
St. Bonaventure University
Abstract
Extraverted and introverted personalities often employ
different coping strategies that are most conducive to their needs. It has been found that introverts tend to be
over stimulated by their surrounding in contrast to extroverts who are found to
be under stimulated in their normal environments (Burger, 2000) . Violanti (1992) found that coping strategies often aid
in deceasing the level of stress in a situation. Using a coping mechanism, regardless if
passive or active helps an individual deal with the situation. The following study was
designed to assess the coping styles used by introverts and extroverts in high and low stress situations. It was predicted
that introverts in highly stressful situations would have low coping scores
indicating passive coping Introverts in lower stress situations would
produce medium coping scores, which indicate that mainly passive coping is used
however some active coping skills would be used. In contrast, extraverts in highly stressful
situations would have high coping scores which indicate purely active coping
and low coping scores in the low level stress situations.
Things get confusing as you progress toward the end of your
abstract.
Just state you are doing a 2( introvert) x2( stress
level) and predicting a main effects (if you are) and an interaction which
should be delineated. Final sentence should say whether your results we
supported by the data.
Introduction
Extraverts
and introverts are two of the major personality types that people are often
characterized Each person is not purely
an introvert or an extravert, but rather fall on a continuum of extroversion
and introversion (Burger, 2000).
Extraverts are known to have more outgoing and optimistic personalities
and tend to be more sociable, active, and carefree (Burger, 2000). People high in extroversion orient themselves
outward and enjoy being social and surrounded by other people and objects
(Arndt, 1974). Introverts are at the
opposite end of the spectrum from extraverts.
People high in introversion are known to be quieter, more thoughtful,
controlled, and careful (Burger, 2000).
According to Carl Jung, introverts orient themselves inward and establish
their behavior based on biased conclusions (Arndt, 1974). In a recent studyIntroverts were found to
withdraw socially after an increase in stress, in a recent study (Peters, 1996).
These differences in extraverts and introverts cause them to cope with
the situations around them differently.
Often
times during stressful situations individuals employ coping strategies used by
people when they feel threatened and the purpose is to ease one’s anxiety. There are many different types of coping
strategies that are often used by people.
The use of a strategy is often dependent upon on the situation
surrounding the person, their personality and one’s own personal preference of
how they may be able to decrease their own anxiety (Burger, 2000). “We sometimes refer to a person’s general
approach to dealing with stress as his or her coping style,” (Burger, 2000
p.147). There are a number of other
variables that determine one’s coping mechanism.
There
are two categories of coping, active coping and passive coping. Emotion focused coping is a type of passive
coping that is directed toward ones feelings and thoughts at the time a problem
or stressful event occur. It is typically used to decrease ones emotional
anxiety regarding a situation (Burger, 2000).
Avoidant coping, which is another type of passive coping, occurs when a
person manages their awareness in order to decrease unfavorable emotions. People often overlook stimuli in order to
minimize their stimulation level and stress level (Appelhans & Schmeck,
2002). Problem-focused is an active
coping strategy that is used to decrease anxiety by dealing with the actual
problem, and therefore dealing with the stress by actively helping the problem (Burger,
2000).
Each
personality has a different manner with which they use to cope with the
situation around them, and each coping strategy used is usually based on the
needs of that personality. The event
surrounding the emotions also has an effect on the type of coping strategy each
personality will engage in. When the
situation presented in the Langerns and Moerth (2003) study had a low level,
passive, specifically avoidance coping skills were applied. This information indicates that the
circumstances surrounding the event, as well as the personality are indicators
of the type of coping, active or passive, that would be employed by the
individual. Introvert and extrovert
respond to situations with behaviors that correspond to their level of arousal,
in order to produce an optimal outcome in a situation. When people were presented with a situation
with a high level of threat; active coping strategies are often used. When the situation presented in the Langerns
and Moerth (2003) study had a low threat level, passive, specifically avoidance
coping skills were applied. This
information indicates that the circumstances surrounding the event, as well as
the personality are indicators of the type of coping , active or passive, that
would be employed by the individual.
Introverts and extroverts respond to situations with behaviors that
correspond to their level of arousal, in order to produce an optimal outcome in
a situation. It had been found that the
coping behaviors for introverts in this study are different than that of
extroverts, and that coping is in fact, related to personality (Gallaghar,
1996). Therefore introverts and
extroverts have different methods of coping and they each apply the coping
method that causes them to have the best performance possible.
Extroverts
have been positively correlated with using adaptive coping styles (Baoyong,
2000). Adaptive coping styles are
methods of coping that are flexible and conform to the needs of the situation
or problem, which does not include avoidance.
Extroversion has been negatively correlated with avoidance coping,
indicating that passive coping is not significantly used by extroverts
(Bosworth, Feaganes, Vitaliano, Mark, and Siegler, 2001). Introversion, in contrast, has been
correlated with maladaptive manners of coping (Baoyong, 2000). These are coping strategies that are not
conducive to the resolution of the problem or situation, which can also be
known as passive coping strategies.
Halammandaris and Power found that neuroticism, or introversion, has
also been found to be associated with passive coping mechanisms (1999). Introversion has, “often (been) equated with
neuroticism,” which indicates that introversion and passive coping are related
(Bradely, 1996). Introverts use modes
of coping that are primarily passive, focused on emotion, and aimed at the
decrease of stress. Extroverts are found
to typically use more active coping strategies.
A
study done in 2000 has found that aggression is negatively correlated with
avoidance coping behaviors (Blair, 2000).
People who tend to be aggressive typically do not use avoidance coping,
a passive coping mechanism (Blair, 2000).
On the other hand, people that are highly neurotic, which is “equated”
with introversion, were found to have low verbal aggression and low
apprehension about communication.
Extraverts, however, view themselves as aggressive, aware, are often
impulsive communicators, and tend to have a tolerance for arguments (McCroskey
& Heisel, 2001). Therefore,
extroversion and aggression are related, and highly aggressive people typically
do not use passive coping strategies.
Introversion was associated with a low level of verbal aggression which
indicates the possibility that they use passive coping. The
choice of passive or active coping strategies are also affected by the level of
stress in a situation. Stowell, Kiecolt,
and Glaser (2001) found that situations of higher stress brought about more
active coping mechanisms in people.
However, lower stress situations were found to be significantly
associated with more passive coping skills.
The level of stress is another variable used to determine the type of
coping strategy a specific personality may employ.
Hypothesis
State main effects and interactions In this study it
was attempted to show that introverts, under high stress situations would have
low overall coping scores because they will employ more passive coping
skills. In a low stress situation
introverts will have a medium coping score which indicates that they will need
to employ more passive coping and very little active coping. Introverts have many personality
characteristics that have been highly correlated with the use of more passive
forms of coping. Extraverts will receive high coping scores because they tend
to use active coping skills in situations of high stress. In low stress situation however, extroverts
would have low coping scores because of the under stimulation that the
extrovert will experience.
Methods
Participants check apa
style pg 307
Forty undergraduate psychology students
participated in this study, twenty extroverts and twenty introverts. Twenty of the
participants were male, and were labeled as introverted or extroverted
accorining to the personality inventory.
Twenty of the female participants were also labled introverted or
extroverted based on the inventory. Each
participant voluntarily signed up for a time to participate. Each subject received extra credit points, to
be determined by professors, for their participation in this study
Measures
The
Eysenck personality inventory was administered to each person (Eysenck &
Eysenck, 1975 as cited in Lu & Chen,1996).
The inventory was used to determine where on the continuum of
introversion/extroversion each participant fell. As each participant was assigned to a group
they were either administered a sheet containing ten easy or ten hard anagrams,
and asked to complete the task. The
purpose of the anagrams was to administer a low amount of stress, using easy
anagrams, or a high amount of stress, using hard anagrams. After the
participants completed or attempted their task, the Strategic Approach to
Coping Scale (SACS) was administered (Hobfall, Dunahoo, Ben-Porath, &
Monnier 1994). This is a valid and reliable
method of assessing each students passive or active coping strategy.
Procedure
The
participants first signed a consent form and were then administered the Eysenck
personality inventory to determine each subjects level of introversion or
extroversion. Each test was then scored
and the participant were then assigned a label of extrovert or introvert, based
on their scores from the personality inventory.
Then, the participants randomly receive a sheet containing ten easy or
difficult anagrams, which manipulated the participants, stress level. After the participants completed the
anagrams, they were administered the SACS (Strategies Approach to Coping
Scale). After completing this inventory
they were given a debriefing statement and were free to leave.
Results
The
results of the study were statistically analyzed using an 2(introversion) x2
(stress levels) between subjects ANOVA (N=40).
Each group (n=10) consisted of one personality (introverts or
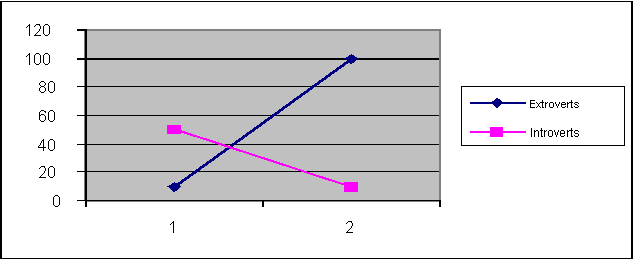
extraverts) exposed to a high or low stress situations. The mean was 52.3 for introverts in low
stress and a mean of 19.8 for introverts in high stress situations. See Table Extroverts had means of 21.6 and
84.4 for low and high stress situations respectively (see Figure 1). After the data was analyzed using an ANOVA
results indicated that there was a signficance regaurding the level of active
or passive coping used by each main effect personality
with F(1,36)=15.561, p< .05.
Stress was also significant factor in predicting the level of main effect active or passive coping with
F(1,36)=12.432, p< .05. An
interaction between ones personailty and the level of stress was also found to
be significant F(1,36)=122.980, p<.05.
These results are concurrent to those predicted.
Discussion
The
results indicate that there is an interaction between the two independent
variable of extroversion/introversion, and their level of stress and the
dependent variable of the type of coping strategy they use. The resutls above indicate that the predicted
hypothesis was found to be significant.
The high levels of stress imposed on introverts cause them to use more
passive coping, and extroverts to use more active coping. Under lower levels of stress introverts had
medium levels of coping which indicated that more passive than active coping
was present. The extroverts were found
to utilize purely passive coping skills under low stress situations.
Concurrent
with the previous research that has been done on personality and coping, and
stress and coping, this research indicates that both have significance in the
prediction of the levels of active or passive coping each would utlize. This research may prove benefical to aid
individuals in selecting coping strategies that would best fit their
personality and stress level of the situation in order to achieve the optimal
outcome. Further research may focus on
specific types of active and passive coping stategies to predict specific
coping rituals.
Your results are way too
brief. Just relax an write what the results mean for the real world and for
research on introversion and stress. Just let it go.
References
apa violations see manual
Appelhans, B.M & Schmeck, R.R
(2002). Learning Styles and Approach
Versus Avoidant Coping During
Academic
Exam Preparation. College Student
Journal, 36. pgs
Arndt, W. B (1974). Theories of Personality. New York Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc.
Baoyong, L. (2000). Ways of coping and
personality. Chinese Journal of
Clinical Psychology, 8, 7-9.
Blair, K.A (2000).
Emotion regulation and aggression: A function of coping style and
emotionality. Dissertation Abstract
International: Section B: The Sciences & Engineering, 61 (2-B) 1108.
Bosworth, H.B; Feaganes, J.R; Vitaliano, P.P; Mark,
D.B & Siegler, I.C (2001).
Personality and coping with a common stressor: Cardiac
catheterization. Journal of
Behavioral Medicine, 24, 17-31.
Bradly, P.J (1996).
Introversion as construct and disposition: A positive assessment and
conceptual analysis. Dissertation
Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences & Engineering, 57,
2205.
Burger, J. M (2000).
Personality. Wadsworth:
Thomas Learning.
Gallagher, D.J (1996).
Personality, coping, and objective outcomes: Extroversion, neuroticism,
coping styles, and academic performance.
Personality & Individual Differences, 21, 421-429.
Halammandaris, K. F & Power, K.G (1999). Individual differences, social support and
coping with the examination stress. A
study of the psychocosial and academic adjustment for first year home
students. Personality &
Individual Differences, 26, 665-685.
Hobfall, S.E; Dunahoo, C.L; Ben-Porath,Y; Monnier, J
(1994). Gender and Coping: The dual-axis
model of coping. American Journal of
Community Psychology,22 (1), 49-82.
Langens, T.A & Moerth, S (2003). Repressive coping and the use of passive and
active coping strategies. Personality
& Individual Differences, 35, 461-473.
Peters, S. L (1996) Introverts in extroverted roles:
How introverted reporters cope. Dissertation
Abstracts International
Section A: Humanities & Social Sciences, 57.
McCroskey, J, C & Heisel, A.D (2001). Eysenck’s BIG THREE and communication traits:
Three correlational studies. Communication
Monographs, 68, 360-366.
Stowell, J.R; Kiecold-Glaser, J.K & Glaser, R
(2001). Perceived stress and cellular
immunity: When coping counts. Journal
of Behavioral Medicine, 24, 323-339.
Violanti, J. M (1992).
Coping strategies among police recruits in a high-stress training
environment. Journal of Social
Psychology, 132.
Table 1 see manual
|
|
Introverts |
Extraverts |
|
High
Stress |
19.8 |
84.4 |
|
Low
Stress |
52.3 |
21.6 |
Figure 2
 ?
?