Taxes,
trophics, habituation, and sensitization

I thought it would be
a good thing, since we are using the “ begin at the most simplest/basic/Emeril
Lagasse 

Model “ to start with
a few examples of Invariant
response--no learning
2
1.) Kinesis Simplest …least complex
An instance where a stimulus produces a
change in the speed or movement irrespective of the direction of the movement.
Woodlouse: Congregates in high humidity and reflexively moves in low humidity.
Doesn't prefers low humidity but just stops moving in high humidity.
2) Taxes: Intermediate complexity
Change in behavior
which is caused as a direct result of a stimulus.
Blood sucker moves
toward warm bodies
earthworms away form
bright light
Moths toward light
and heat---------late summer night close to a street light or house light swarming--------------bees
3) Sign stimuli: SS> IRM> FAP
Most complex
gull and SS red spot
on beak
Fixed and leaned
responses.. An
example of an innate behavior can be seen in Herring gull chicks, which were
studied by Tinbergen. Adult females have a red spot on their beak. Chicks
instinctually peck at this spot, which stimulates the female to regurgitate and
feed the young chick. The red spot is the SS, and it releases the pecking FAP
in the chick.
Monarch
Migration
much of their bodies
in contact with a surface as possible. In a burrow or wall of a
3
Habituation and Sensitization Single Event
1. Presentation of the stimulus alone.
=> habituation, sensitization
(non-associative learning).
2.Presentation of the stimulus in relation
to another stimulus. => classical
conditioning (associative learning)
3.Presentation of the stimulus in relation
to some of the organisms own
behavior. => operant conditioning
(associative learning)
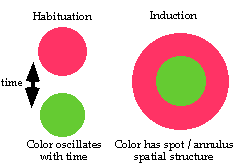
Habituation
(definition) -- Given that a particular stimulus elicits a response,
repeated applications
of the stimulus result in decreased response. The decrease is
usually a negative
exponential function of the number of stimulus
presentations. Habituation Film
Habituation is a
reduction in a previously-displayed response when no reward or punishment
follows. If you make an unusual sound in the presence of the family dog, it
will respond - usually by turning its head toward the sound. If the stimulus is
given repeatedly and nothing either pleasant or unpleasant happens to the dog,
it will soon cease to respond. This lack of response is not a result of Habituation.
2. Spontaneous
Recovery -- If the stimulus is withdrawn following habituation
training, the
response tends to recover over time.
Pennsylvania—Johnstonwn, Room, Terrorism, sulphur water, Peoria and PBR
Beer, Your examples. Studies.
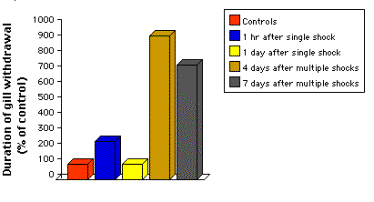
Effects of the
repeated presentation of an eliciting
stimulus
4
Characteristics of
habituation effects
Sensitization
Sensitization
is an increase in the response to an innocuous stimulus when that stimulus
occurs after a punishing stimulus or painful stimulus. .
An
example: Telephone, grades, doctor, blood test, snake
in room bear in room CLAP
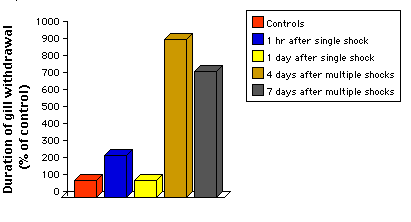
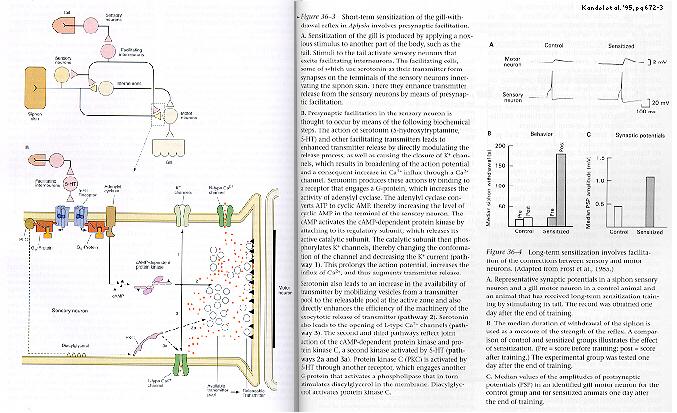
 When the siphon of the sea
slug Aplysia is gently touched, the animal withdraws its gill for a brief
period. However, if preceded by an electrical shock to its tail, the same
gentle touch to the siphon will elicit a longer period of withdrawal.
When the siphon of the sea
slug Aplysia is gently touched, the animal withdraws its gill for a brief
period. However, if preceded by an electrical shock to its tail, the same
gentle touch to the siphon will elicit a longer period of withdrawal.
The sensitization response to a single shock (blue bar) dies out after about an hour, and returns to baseline after a day (yellow). So it is an example of short-term memory.
However,
it the animal is sensitized with multiple shocks given over several days, its
subsequent response to a gentle touch on the siphon is
If you have ever
burnt one on your fingers you might have noticed
that if you run your
hands under warm water, your burnt finger
will hurt, even if it
is the day after you burnt it. The warm water
normally does not
cause any pain, but after burning your finger, it
is sensitized. Now the warm water causes pain.
Page 5
Habituation
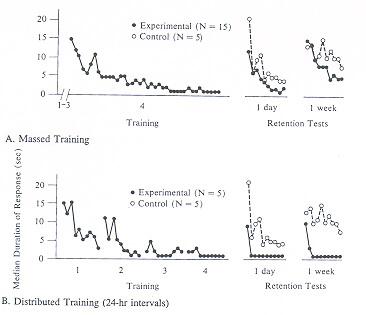
Sensitization
Next: Two
event Learning—Wednesday

