The Effect of Introversion and Extroversion and Level of Vigilance on
Alcohol Consumption
Kerry O’Mahoney
Personality type:
Introverts:
described as people who are generally quiet, reserved and thoughtful. They are
thought to have relatively higher levels of brain arousal, which causes them to
shy away from over stimulating social environments.
Extroverts:
described as people who are generally sociable, active and outgoing.
Coping Style:
Vigilant coping
style: are more likely to exaggerate threatening information in situations
of high anxiety and stress and are more likely to seek medical attention. They
are also highly disposed to preparation and preventative control and show a
need for as much information as possible before beginning a task.
Avoidant Coping Style:
prefer not to be aware of negative
information and therefore distract themselves from all negative situations.
This behavior is associated with some negative characteristics such as
procrastination, problems with time management, task aversiveness,
thrill seeking, and intolerance to arousal.
Article #1:
Research found that avoidance coping predicted an increase
in alcohol consumption. Substance abuse can be viewed as an avoidant coping
mechanism utilized when adaptive coping alternatives are not available. (Litman, Eiser, Rawson, and Oppenheim 1979)
Article #2:
Increased Alcohol consumption is positively correlated with
sociability and extroversion
(Cook, 1998)
My Study: Do
Extroverts with avoidant coping behavior consume alcohol in a larger quantity
and with more frequency?
IV: Level of vigilance( avoidant or
vigilant)
IV: Personality Type (Introvert or extrovert)
DV: Quantity and frequency of consumption
2x2 interaction
Procedure: Fill out three questionnaires
1. Ways of coping checklist
2. Eysenck personality inventory
3. The Q-F-V
Predictions:
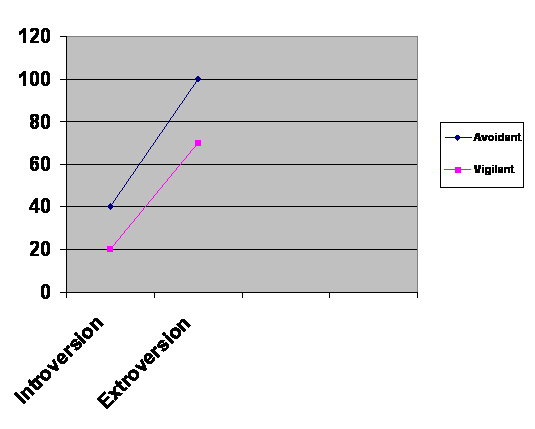
1. An interaction between personality type and coping behavior (avoidant or vigilant)
2. A Main effect of coping behavior on alcohol consumption
Hypothesis:
Extroverted avoidant subjects will consume the most alcohol
of the four groups. Extroverted Vigilant subjects will consume less that
Extroverted Avoidant but more than introverted subjects. Introverted avoidant
subjects will consume more than introverted vigilant subjects, who will consume
the least of the four groups.
|
|
Introversion |
Extroversion |
|
Avoidant |
40 |
100 |
|
Vigilant |
20 |
70 |