222@22 Applications of Skinnerian Learning
Instrumental Learning Ib
1) law of effect and Thornkike/Watson(Little Albert) : The Law of Effect (E. L. Thorndike)
“Of several responses made to the same situation, those which are accompanied or closely followed by satisfaction to the animalwill, other things being equal,
be more firmly connected with the situation, so that, when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur;
those which
are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other
things being equal, have their connections
with that situation
weakened, so that, when it recurs, they will be less likely to occur. The greater
the satisfaction or discomfort,
the greater the strengthening or weakening of the
bond." (Thorndike, 1898, p.244).
2) Enter Skinner
Operant Leaning
Learing involves sequencing behavioral units
(R1-S1) via successive approximations such that
through shaping the learner will receive a desirable consequence after
the sequence is complete. Example (lab and non-lab)
Page 2
Lab example: Teach rat to bar press: rats do not come
into the world with the capacity to reflexively bar press to receive a reward
so therefore you have to train that animal via successive approximation
sequence training 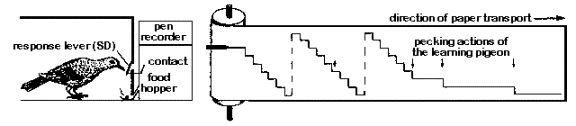 (shaping)
(shaping) 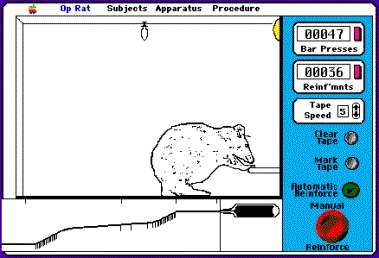
Page3
Behavioral units
R1-S1 placed in Skinner box and runs
R2-S2 moves toward water source and receives water (CS-UCS) Magazine training
R3-R3 Turns in the direction of bar press (RFT)
R4-S4 Moves in the direction of bar press (RFT)
R5-S5 Touches right paw on bar press (RFT)
R6-S6 Places both paws on bar press (RFT)
Realize that all responses that do not lead to a bar press-like response are
not reinforced or extinguished.
R7-S7 Push bar down and get (RFT)
Page 4
 .
.
Piano Playing, free throws, studying, driving: Shaping, chaining, and successive approximation
Pg 5 Monkey l eventually help disabled at home 


Helping Hands has placed some 230 monkeys in foster
care nationally and matched 45 with people who have quadriplegia. The
Koblinskis are one of five Michigan families providing foster care for a
capuchin. Because these
monkeys live to the age of 35-40, they can be long-term companions to
quadriplegics. For a monkey to successfully coexist with a quadriplegic,
the animals must be socialized from an early age with
Page6
humans. When socialization is complete, the animals are sent to Helping Hands training center in Boston,which is affiliated with Boston University School of Medicine for nine months of training.
They are taught to respond to a beam of light that the disabled ownerdirects from a mouth-operated laser pointer. The owner shines the beam on an object he/she wants the monkey to manipulate.
The monkeys learn to perform tasks such as fetching drinks from a refrigerator, transferring items to and from the microwave. They are taught to place books on a reading stand and put cassettes into a VCR. They can retrieve fallen mouthsticks or other tools.
1)
Contiguity R1 > S1 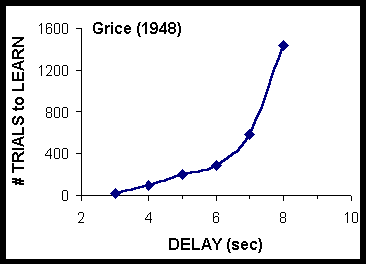
2) Superstition: In six out of eight cases the resulting responses were so clearly defined that two observers could agree perfectly in countinginstances. One bird was conditioned to turn counterclockwise about the cage, making two or three turns between reinforcements.Another repeatedly thrust is head into one of the upper corners of the cage. A third developed a "tossing" response, as if placingits head beneath an invisible bar and lifting it repeatedly." (p. 168)
Page 6
3) Contingency
4)
Extinction 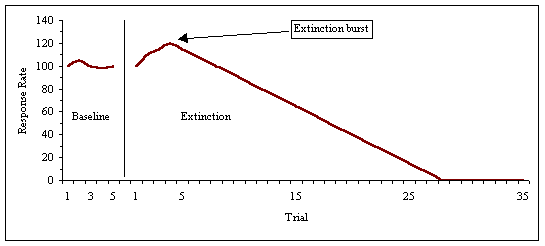
5) Spontaneous Recovery
6) Positive Reinforcer
A positive reinforcer is an appetitive event whose presentation follows an operant response. The positive
reinforcer increases the likelihood of that behavior occurring again under the same circumstances.